In this section, you will learn about the configurations and libraries that affect an entire application's accessibility.
Lang Attribute
Declaring the language of the HTML document allows users to better understand your content.
Both assistive technologies and conventional user agents can render text more accurately when the language of the Web page is identified. Screen readers can load the correct pronunciation rules. Visual browsers can display characters and scripts correctly. Media players can show captions correctly. As a result, users with disabilities will be better able to understand the content. WCAG Success Criterion 3.1.1: Intent
A primary language should be defined on the <html> element's lang attribute. For existing Ember apps, a developer may edit the index.html file or leverage ember-intl.
The html element may not have multiple lang values. If an element contains content in a language different from the primary, then you can provide the element its own lang attribute.
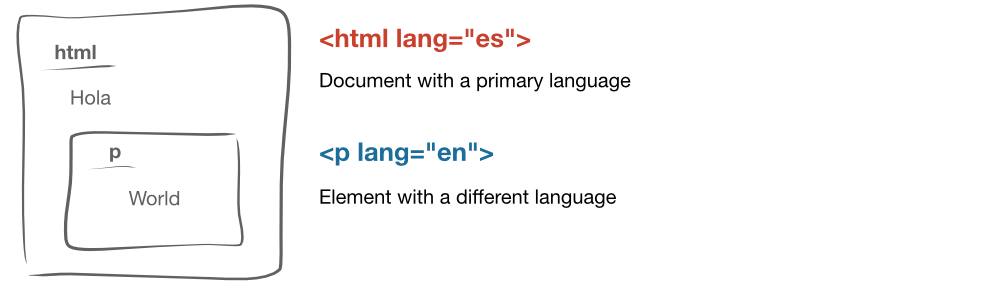

Configurations
Application template wrapper
You can simplify your markup and increase accessibility at the same time by configuring application-template-wrapper.
If you are using the application template wrapper enabled (default state), then you would need to add certain aria roles to your landmark regions, even if you are using native HTML elements, because those regions are not the direct child descendant of the body element (they are the children of the div that wraps the Ember app).
If you disable the application template wrapper, you will not need to add role attributes to your landmark regions when they are the direct descendant of the body element, and they are using native HTML elements. This is the preferred approach for accessible applications.
To disable this feature and improve your app's accessibility:
ember feature:disable application-template-wrapperApplication Template Wrapper Disabled (preferred)
<body>
<header></header>
<main></main>
<footer></footer>
</body>Application Template Wrapper Enabled
<body>
<div class="ember-view">
<header role="banner"></header>
<main role="main"></main>
<footer role="contentinfo"></footer>
</div>
</body>
Ember applications vs role=''application''
An important thing to note in this section is this: "application" in Ember development and "application" in landmark roles have two very different meanings.
The TL;DR? Don't use role="application" until you have done your research and know exactly how it is to be used correctly (if at all). There are very few use cases where the role of application is appropriate.
Read more about it: https://www.a11yproject.com/posts/2013-02-09-how-to-use-application-role/
Accessibility addons
Any addon that will provide UI elements to the application should be evaluated for accessibility before use.
There are some existing Ember addons that may help you make your app more accessible. Each addon should be evaluated for its own usefulness and merit- you may find in some instances, that it would be better to implement the ideas presented in the addon in your own application.
Here are some examples of accessibility-focused addons created by many people throughout the Ember community:
- ember-a11y-landmarks - Ember addon to help with landmark roles for better accessibility
- ember-component-focus - A mixin for adding methods to your Ember components that help you manage the currently focused element.
- ember-gestures - Ember Gestures provides an easy way to use gestures by making it simple to define and use HammerJS managers and recognizers throughout your app.
- ember-steps - Declarative create wizards, tabbed UIs, and more
- ember-page-title - Page title management for Ember.js Apps
- ember-self-focused - Focus on route on transition
- ember-keyboard - An Ember.js addon for the painless support of keyboard events
- ember-a11y-testing - A suite of accessibility tests that can be run within the Ember testing framework
- a11y-announcer - An accessible ember route change announcer
- ember-template-lint - linter for Ember templates
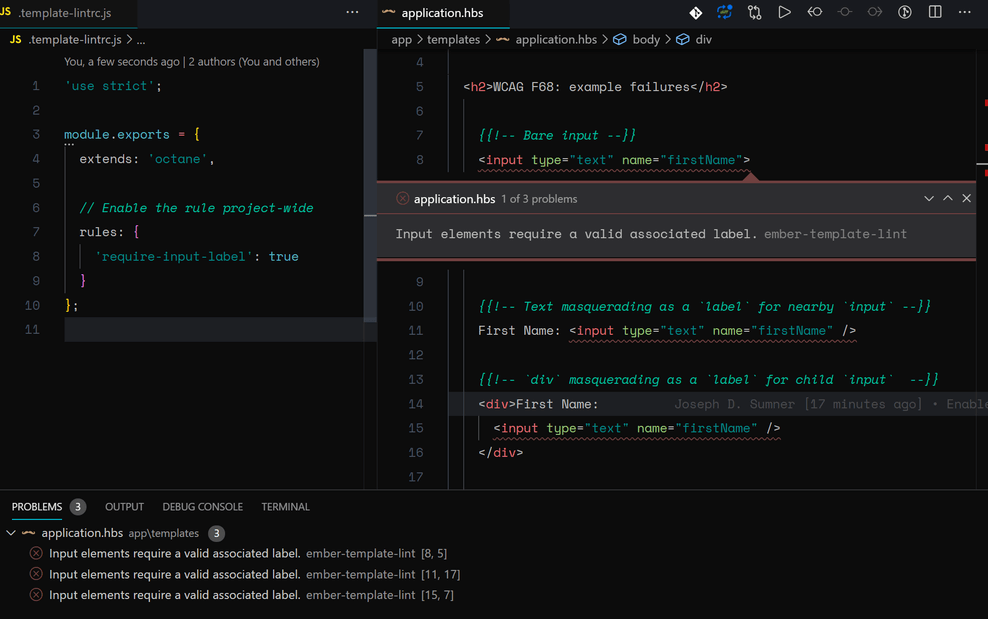
While there are quite a few moving parts, here's a cheat sheet to get you started: Accessibility Cheat Sheet